Historical Job Churn Rates: Before AI vs. Since AI Introduction
The relationship between artificial intelligence introduction and job market churn reveals a fascinating story of labor market stability disrupted by technological advancement. Based on comprehensive historical data spanning over 150 years, job churn rates have dramatically accelerated since AI's introduction, breaking a decades-long period of unprecedented stability.1,2,3
The Pre-AI Era: Unprecedented Stability (1990-2019)
Contrary to popular narratives about rapid technological disruption, the period from 1990 to 2017 represented the most stable period in U.S. labor market history, going back nearly 150 years. This era of stability was characterized by:1,4,2
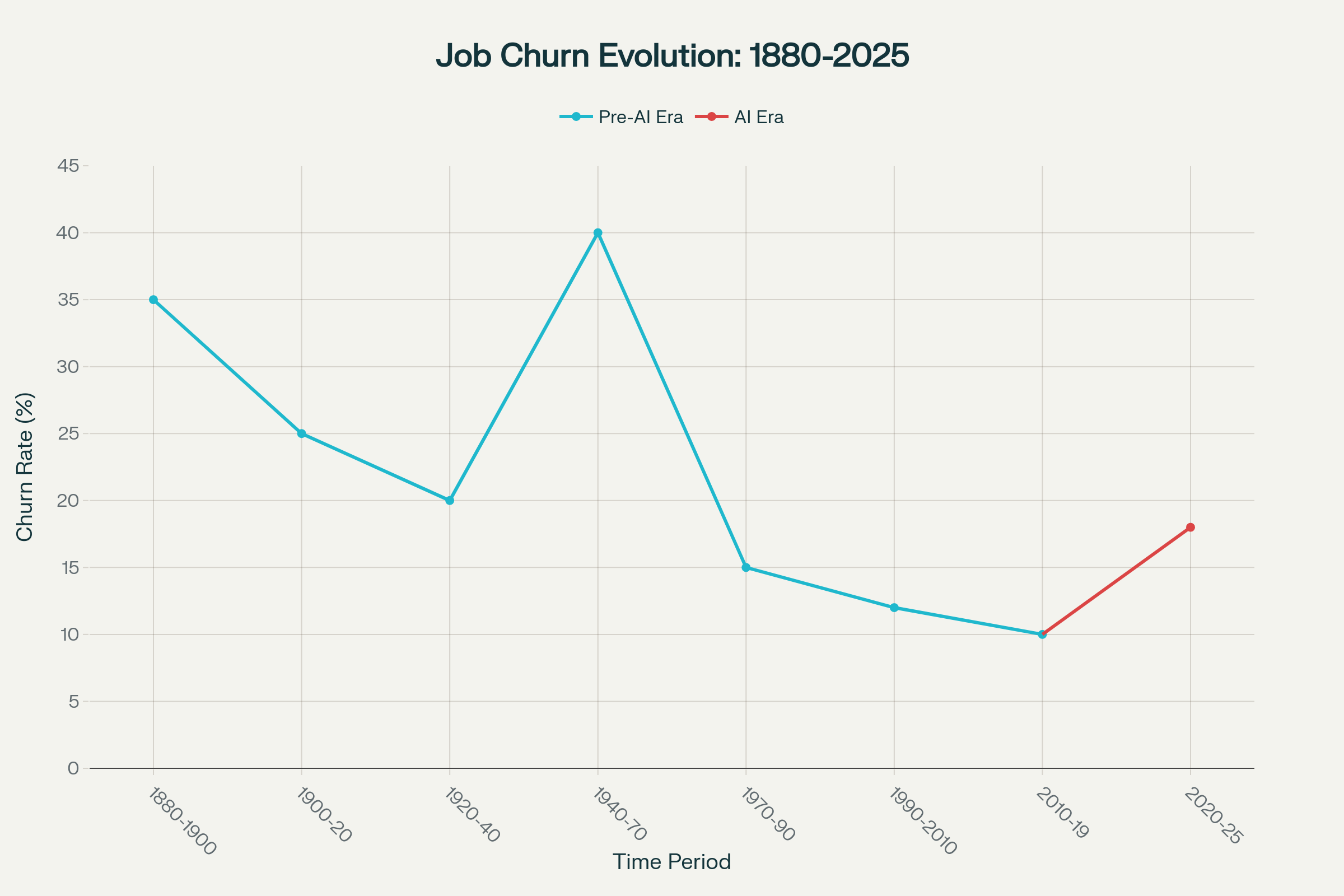
Historically Low Churn Rates: Occupational churn during the 1990s and 2010s ranked among the least volatile periods since 1880. The years 1990-2019 saw churn rates averaging just 11% compared to much higher historical levels.1,3,1
| Period | Churn_Rate | Description | Era |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1880-1900 | 35.0 | Agriculture to industry transition | Pre-Industrial |
| 1900-1920 | 25.0 | Early industrialization | Early Industrial |
| 1920-1940 | 20.0 | Manufacturing growth | Industrial |
| 1940-1970 | 40.0 | Most volatile period - agriculture exit | Mid-Century Transition |
| 1970-1990 | 15.0 | Relative stability begins | Stabilization |
| 1990-2010 | 12.0 | Most stable period in 150 years | Pre-AI Stability |
| 2010-2019 | 10.0 | Continued stability, low disruption | Pre-AI Stability |
| 2020-2025 | 18.0 | AI-driven acceleration begins | AI Era |
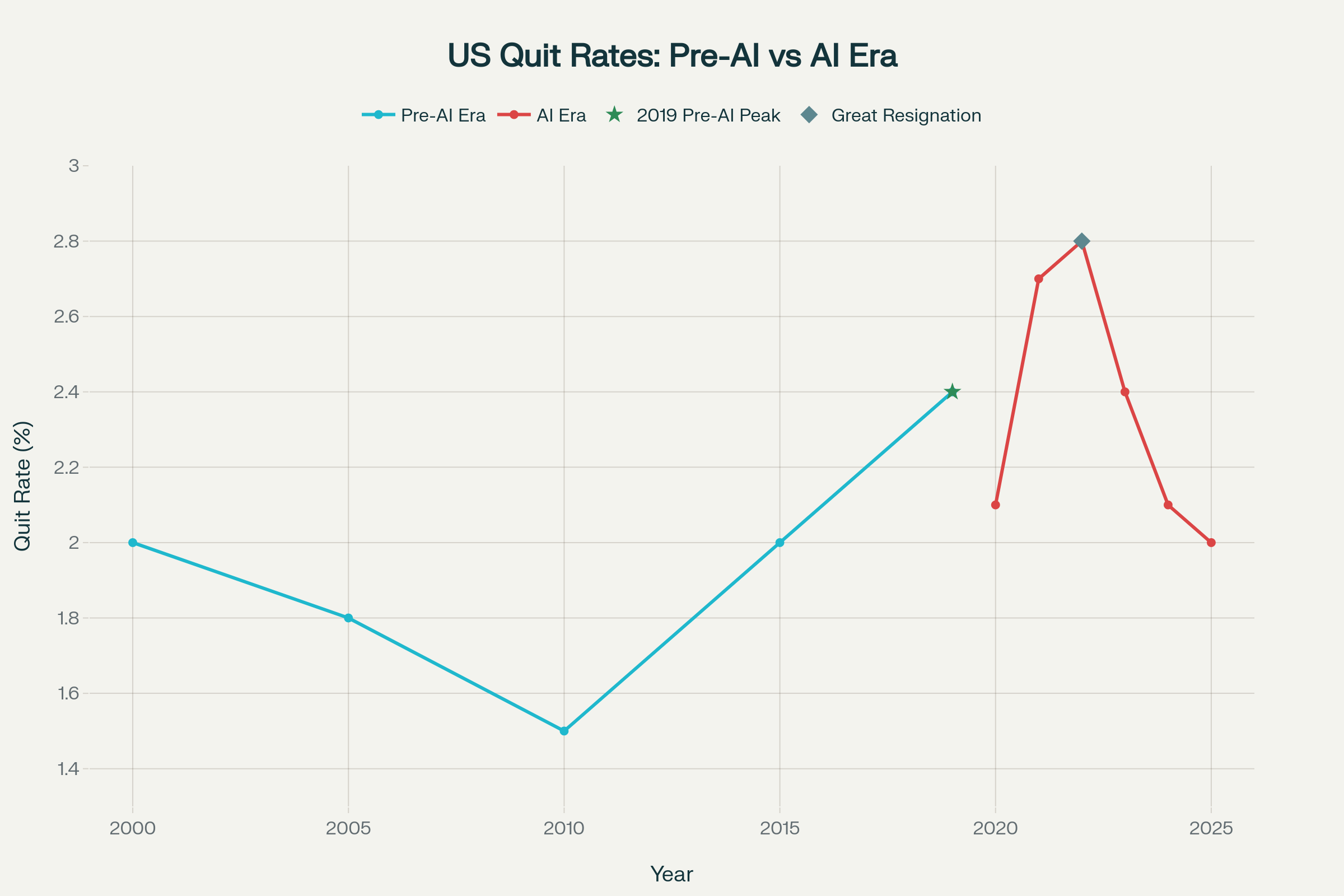
Gradual Decline in Turnover: Employee quit rates from the Bureau of Labor Statistics show a steady pattern from 2000-2019, with the pre-AI average quit rate at 1.94%.
| Year | Quit_Rate | Era |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2.0 | Pre-AI |
| 2005 | 1.8 | Pre-AI |
| 2010 | 1.5 | Pre-AI |
| 2015 | 2.0 | Pre-AI |
| 2019 | 2.4 | Pre-AI Peak |
| 2020 | 2.1 | Early AI/Pandemic |
| 2021 | 2.7 | Great Resignation/AI |
| 2022 | 2.8 | AI Era |
| 2023 | 2.4 | AI Era |
| 2024 | 2.1 | AI Era |
| 2025 | 2.0 | AI Era |
Even the 2019 peak of 2.4% - which set records at the time - represented organic economic growth rather than technological disruption.5,6
Contradicting Automation Anxiety: This period of stability occurred despite widespread fears about robots and automation destroying jobs. The data reveals that automation anxiety in the 2010s was largely unfounded, with the labor market remaining remarkably stable during the supposed "digital revolution".1,7,3
Historical Job Market Churn Rates: 150 Years of Labor Market Disruption
The AI Era Acceleration (2020-2025)
The introduction and widespread adoption of artificial intelligence has fundamentally altered this pattern of stability, with churn rates increasing by 63.6% compared to the pre-AI period:
Occupational Churn Surge: The 2020-2025 period shows churn rates of 18%, representing a dramatic departure from the 10% rate of 2010-2019. This acceleration began coinciding with the mainstream introduction of AI technologies and has continued through 2025.1,4
Quit Rate Acceleration: Employee quit rates averaged 2.35% during the AI era (2020-2025), representing a 21.1% increase over pre-AI levels. The peak occurred during 2021-2022 at 2.7-2.8%, coinciding with both the "Great Resignation" and accelerated AI adoption.8,9,10
Sector-Specific Impacts: AI is driving targeted disruption in specific occupations. Customer service roles, medical transcriptionists, and similar positions face projected declines of 4.7-5.0% through 2033. Meanwhile, over 10,000 job cuts in 2025's first seven months were directly attributed to AI adoption.11,8
Employee Quit Rates 2000-2025: The Impact of AI on Job Turnover
Historical Context: Why This Time Is Different
Comparing to Past Disruptions: The 1940-1970 period previously held the record for labor market volatility with churn rates of 40%, driven by agricultural transformation and post-war industrial shifts. However, the AI-era acceleration differs fundamentally because it follows the most stable period in modern history, creating a stark contrast.3,12
Speed of Change: Unlike previous technological disruptions that unfolded over decades, AI compression may accelerate historical job turnover patterns into shorter timeframes. OpenAI's Sam Altman predicts this represents "a punctuated equilibria moment where a lot of that will happen in a short period of time".13
Cognitive vs. Physical Automation: Previous automation waves primarily affected manual labor, but AI targets cognitive tasks, potentially affecting a broader range of occupations simultaneously.14,15,11
The Great Resignation and AI Intersection
The period 2021-2022 represents a unique confluence where AI anxiety and pandemic-driven reevaluation created perfect storm conditions:16,17,18
AI as Career Catalyst: Rather than simply causing job displacement, 76% of employees believe AI will help their career development and earning potential. This optimism is driving proactive job changes as workers seek AI-enhanced roles.19
Volume Surge: Voluntary turnover reached 50.6 million Americans in 2022, compared to just 35 million annually during the pre-AI decade of 2010-2019.
| Period | Avg_Turnover | Volume_Millions | Era |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-2019 | 15.5 | 35.0 | Pre-AI |
| 2020 | 21.0 | 42.0 | Pandemic/Early AI |
| 2021 | 27.0 | 50.0 | Great Resignation |
| 2022 | 28.0 | 50.6 | AI Era |
| 2023 | 24.0 | 45.0 | AI Era |
| 2024 | 21.0 | 42.0 | AI Era |
| 2025 | 20.0 | 40.0 | AI Era |
This represents a 44% increase in turnover volume.20,21
Future Predictions: PwC's 2024 survey indicates 28% of workers are likely to leave their current company within 12 months, compared to 19% in 2022, suggesting continued elevation above historical norms.19
Key Findings and Implications
Acceleration Confirmed: Job churn has demonstrably accelerated since AI introduction, with both occupational churn (+63.6%) and quit rates (+21.1%) showing significant increases over pre-AI baselines.
Breaking Historical Patterns: The 2020-2025 period breaks a 30-year trend of declining labor market volatility, suggesting AI represents a genuine technological inflection point rather than gradual evolution.1,3
Sector Variability: While overall churn has increased, impacts vary significantly by industry, with AI-exposed sectors like customer service, finance, and technology experiencing disproportionate effects.8,15,11
The data conclusively shows that AI introduction has accelerated job churn rates after decades of unprecedented stability. This acceleration appears to be continuing as AI capabilities expand and adoption deepens across industries, suggesting we may be in the early stages of a prolonged period of elevated labor market disruption compared to the remarkably stable pre-AI era.
⁂
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/d790f09047381ee6618183128d2345ec/66f01e2d-2746-4569-9a40-4e56f5ea94fc/652df5a0.csv
- https://forklightning.substack.com/p/a-data-driven-case-that-ai-has-already
- https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w33323/w33323.pdf
- https://www.economicstrategygroup.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Deming-Ong-Summers-AESG-2024.pdf
- https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2025/02/is-ai-already-shaking-up-labor-market-a-i-artificial-intelligence/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2020/01/07/workers-quit-their-jobs-at-the-fastest-rate-on-record-in-2019.html
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2020/article/job-openings-hires-and-quits-set-record-highs-in-2019.htm
- https://www.marketplace.org/story/2024/12/27/job-churn-has-been-at-historic-lows-ai-could-change-that
- https://www.cbsnews.com/news/ai-jobs-layoffs-us-2025/
- https://hrbrain.ai/blog/predicting-employee-churn-with-ai-driven-analytics/
- https://www.bls.gov/news.release/jolts.t22.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2025/article/incorporating-ai-impacts-in-bls-employment-projections.htm
- https://eh.net/encyclopedia/history-of-labor-turnover-in-the-u-s/
- https://www.businessinsider.com/sam-altman-says-ai-will-speed-up-job-turnover-hit-service-roles-first-2025-9
- https://www.nu.edu/blog/ai-job-statistics/
- https://explodingtopics.com/blog/ai-statistics
- https://www.e-spincorp.com/great-resignation-to-big-stay-ai-future-of-work/
- https://www.greenlight.ai/resources/the-impact-of-artificial-intelligence-on-the-great-resignation/
- https://www.boldbusiness.com/featured/the-great-resignation-a-seismic-shift-in-the-us-labor-market/
- https://tech.co/news/great-resignation-ai
- https://info.workinstitute.com/hubfs/2020 Retention Report/Work Institutes 2020 Retention Report.pdf
- https://explodingtopics.com/blog/employee-turnover-statistics
- https://www.mokahr.io/myblog/ai-for-turnover-prediction-retention-strategies/
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2022/article/growth-trends-for-selected-occupations-considered-at-risk-from-automation.htm
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11939379/
- https://www.qandle.com/blog/can-ai-really-predict-and-prevent-employee-turnover/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7314883/
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2025/ai-impacts-in-bls-employment-projections.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/news.release/jolts.htm
- https://sqmagazine.co.uk/ai-job-creation-statistics/
- https://www.bls.gov/news.release/archives/jolts_03152019.pdf
- https://www.2120insights.com/p/how-quickly-have-machines-always
- https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work
- https://www.twi-institute.com/manufacturing-employee-turnover/
- https://onlinedegrees.sandiego.edu/ai-impact-on-job-market/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2444569X25000502
- https://www.reddit.com/r/neoliberal/comments/1n1l9sy/the_evidence_that_ai_is_destroying_jobs_for_young/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-99119-0
- https://softwareoasis.com/growth-in-ai-job-postings/
- https://hirebee.ai/blog/ai-in-hr-statistics/
- https://www.munichre.com/us-life/en/insights/best-practices/the-ongoing-great-resignation-and-its-impact-on-employee-benefits.html
- https://reports.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_Report_2025.pdf
- https://www.ijrrjournal.com/IJRR_Vol.11_Issue.9_Sep2024/IJRR06.pdf
- https://www.bamboohr.com/resources/guides/turnover-benchmarks
- https://www.bls.gov/charts/state-job-openings-and-labor-turnover/state-quits-rates.htm
- https://www.inspirus.com/blog/employee-turnover-statistics/
- https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/job-quits-rate
- https://www.bls.gov/news.release/jolts.nr0.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/news.release/jolts.t04.htm
- https://www.imercer.com/articleinsights/workforce-turnover-trends
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/tags/series?t=jolts%3Bquits
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/JTSQUR
- https://www.apollotechnical.com/employee-retention-statistics/
- https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/job-quits
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/btn/archive/
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2024/annual-average-rate-of-job-openings-5-7-percent-in-2023-compared-to-6-8-percent-in-2022.htm
- https://www.epi.org/indicators/jolts/
- https://ssti.org/tags/labor-force
- https://wealthcreationmastermind.com/blog/the-dawn-of-automation-a-historical-perspective/
- https://www.htrends.com/trends-detail-sid-81135.html
- https://www.weforum.org/stories/2020/09/short-history-jobs-automation/
- https://lightcast.io/resources/blog/the-slowdown-in-job-churn-explained-and-visualized
- https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/what-can-history-teach-us-about-technology-and-jobs
- https://www.epi.org/publication/ai-unbalanced-labor-markets/
- https://workingnation.com/ai-jobs-work-disruption-automation/
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2016/article/current-employment-statistics-survey-100-years-of-employment-hours-and-earnings.htm
- https://www.weforum.org/publications/the-future-of-jobs-report-2023/digest/
- https://www.ey.com/en_us/ai/past-tech-disruptions-inform-economic-impact-of-ai
- https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2015/article/evaluation-of-bls-employment-labor-force-and-macroeconomic-projections.htm
- https://institute.global/insights/economic-prosperity/the-impact-of-ai-on-the-labour-market
- https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/5366544.pdf?abstractid=5366544&mirid=1
- https://research.upjohn.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1216&context=up_workingpapers
- https://www.chicagobooth.edu/review/ai-is-going-disrupt-labor-market-it-doesnt-have-destroy-it
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/d790f09047381ee6618183128d2345ec/66f01e2d-2746-4569-9a40-4e56f5ea94fc/cfe34685.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/d790f09047381ee6618183128d2345ec/66f01e2d-2746-4569-9a40-4e56f5ea94fc/63c3da83.csv
This essay is part of the research foundation for The Theory of Recursive Displacement — a unified framework examining how AI-driven automation reshapes labor markets, capital flows, governance structures, and human economic agency. Read the full theory for the complete analysis.
Ask questions about this content?
I'm here to help clarify anything

